
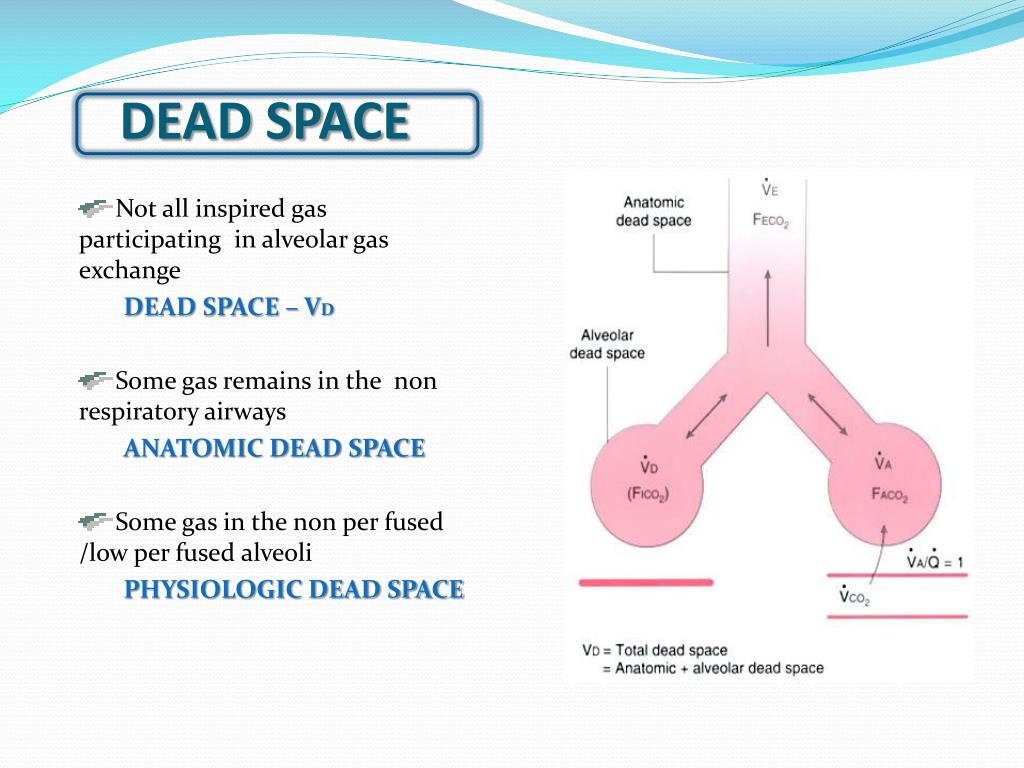
Minute ventilation ( V̇ E the subscript ‘E’ denotes ‘exhaled’) is the total ventilation in one minute (units: L/min).
At this point, it is helpful to define minute ventilation and alveolar ventilation : V D /V T is a common way to quantify dead space. The fraction of the tidal volume that does not contribute to gas exchange is known as dead space fraction (V D /V T where V T = tidal volume and V D = dead space volume). A certain amount of dead space is normally present in every person (this is known as anatomical dead space: see below). This concept can be extended to include factors that cause a dead space effect. Simply put, dead space represents the volume of ventilated air that does not participate in gas exchange.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
